Newest Articles
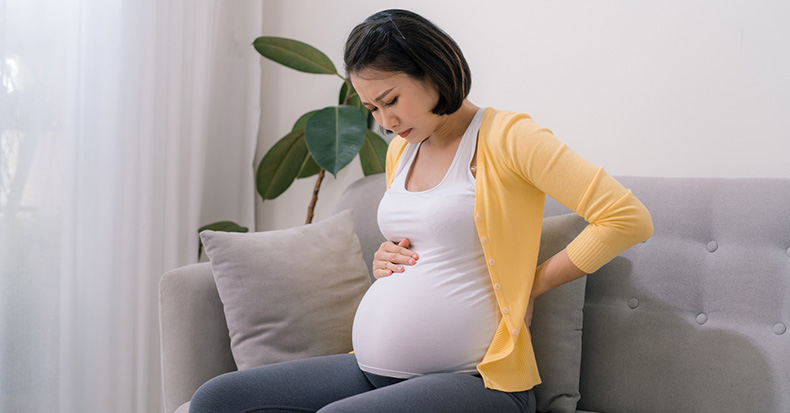
In Part 1 of this series, we discussed the many aspects of pregnancy that contribute to low back pain (LBP) including hormonal, chemical, biomechanical, and psychological changes that occur throughout pregnancy. In Part 2, we looked at the results of several studies showing that chiropractic care can help reduce low back pain (LBP) both during [..]
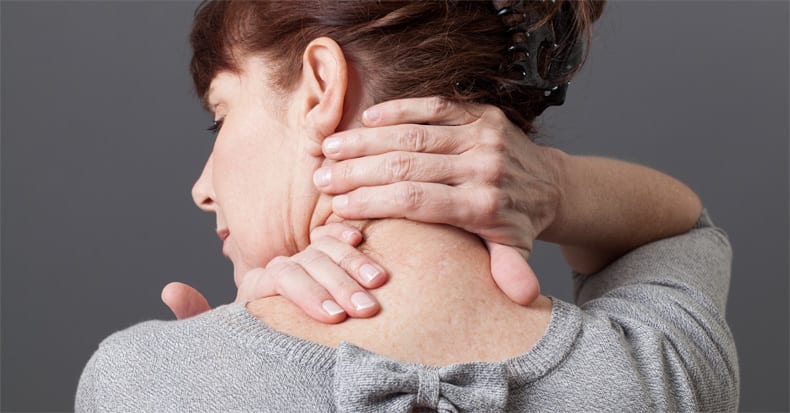
Neck pain can arise from a multitude of causes, from trauma like sports injuries and car accidents to just sleeping in an awkward position. It can also arise from non-traumatic causes like stress, anxiety, or depression. In the past, we’ve noted how forward head posture can increase the risk of neck pain and headaches. Suffice [..]
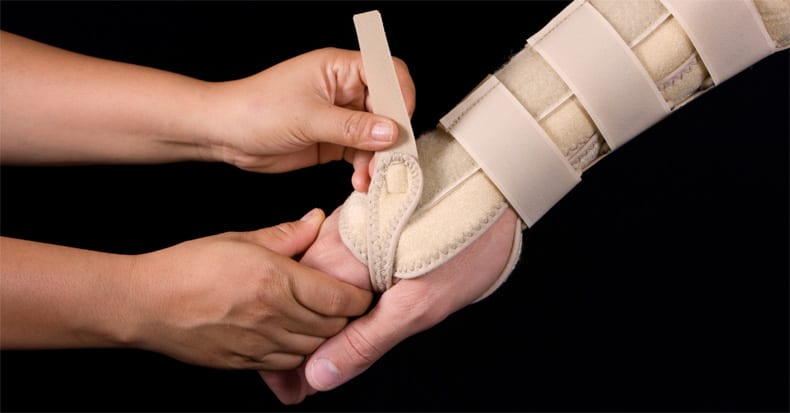
Wrist splints are often a beneficial form of CTS self-care, as they can assist in relieving the pressure within the carpal tunnel by restricting wrist flexion and extension. Because we cannot control the position of our wrist during sleep and the pressure on the nerve worsens the more it bends forwards or backwards, splints are [..]
WHAT IS IT? Iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS) is one of the most common causes of hip and/or knee pain among athletes. The pain is caused from swelling or inflammation of a muscle group (including the tensor fascia lata or TFL, gluteus medius, and minimus muscles), the tendons that attach muscles to the knee or hip, [..]
The terms “whiplash” and “neck strain” are often used interchangeably, though there's debate about whether this is appropriate. Let’s take a closer look at the differences between these two common descriptions of neck pain...
The term “strain” technically means a stretch injury to a muscle and/or the tendon that attaches muscle to bone. The terms [..]
Last month, we discussed four factors that increase a woman's risk for back pain: a wider pelvis (resulting in greater pelvic instability due to knock-knee effect); breast size, mass, and weight; hormone levels and variability during menstruation and menopause; and adolescent growth spurts that can trigger idiopathic scoliosis three-times more commonly in women than men. [..]
The Evidence Continues to Grow
The American opiate crisis and its resulting heroin/fentanyl addiction epidemic began in 1980 when the prestigious medical journal, The New England Journal of Medicine, indicated that “less than one percent” of patients given opiate drugs for pain became addicted (1). Sadly, this statistic was not based on valid scientific data. It [..]
Back pain can become both more frequent and more intense as a pregnancy enters into the second and (especially) the third trimester. This is because the biomechanical changes that accompany pregnancy occur too fast for the body to properly adapt.
Besides the usual suggestions of bed rest, taking frequent breaks, using cold packs, and the [..]
Migraines affect approximately 15% of the general population and are usually managed by medication. However, this traditional treatment approach is not well tolerated by some migraine sufferers due to side effects. Additionally, some people prefer to avoid the risks associated with taking some medications over the long term.
A systematic literature review of randomized controlled [..]
There are nine tendons that pass through the carpal tunnel at the wrist that connect the forearm muscles to the palm-side of the fingers. These tendons are encased in sheaths, and friction and heat can build-up inside these sheaths, leading to swelling, pressure, and pain (especially during fast, repetitive tasks). As the swelling increases and [..]
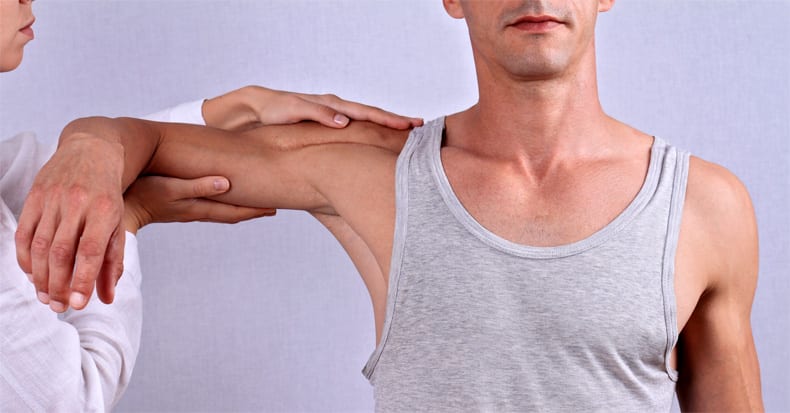
Shoulder pain can arise from a multitude of places—from joints, muscles, tendons, and bursa in and around the shoulder region as well as from more distant locations like the neck, upper back, or even referred pain from the gall bladder. The onset of shoulder pain is highly variable as it can arise without an obvious [..]
Researchers have observed a phenomenon called “central sensitization” (CS) that is common in patients who have long-term, chronic pain following trauma such as whiplash. With CS, the patient's ability to feel pain is abnormally high or hypersensitive, so when pain from pressure, temperature, electrical, or other sources is applied to the skin, they feel it [..]